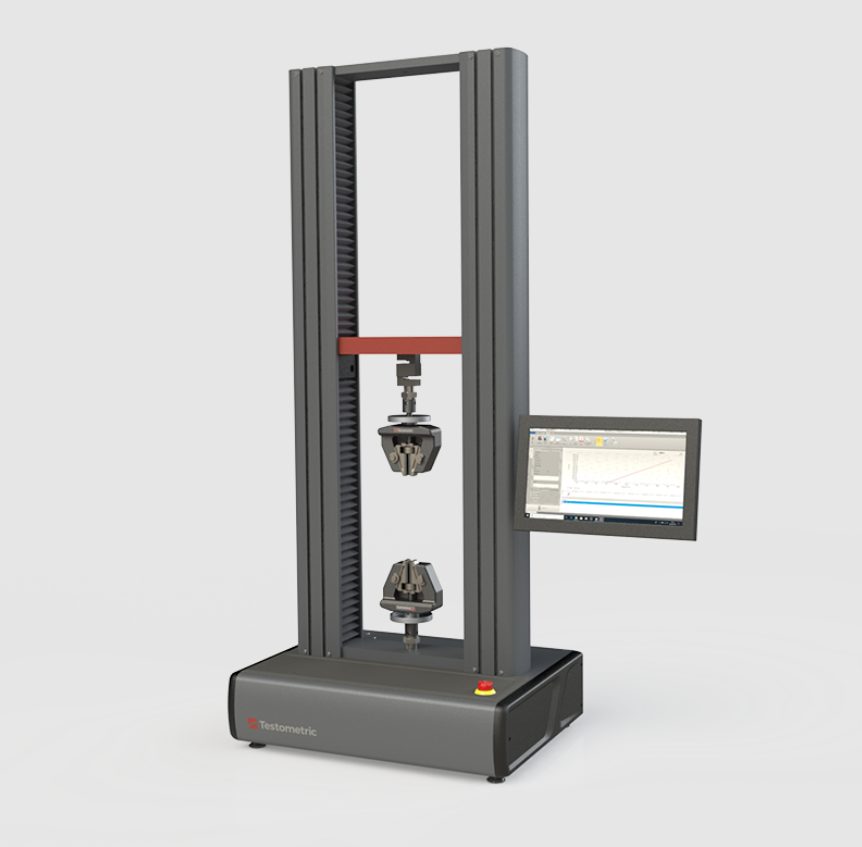
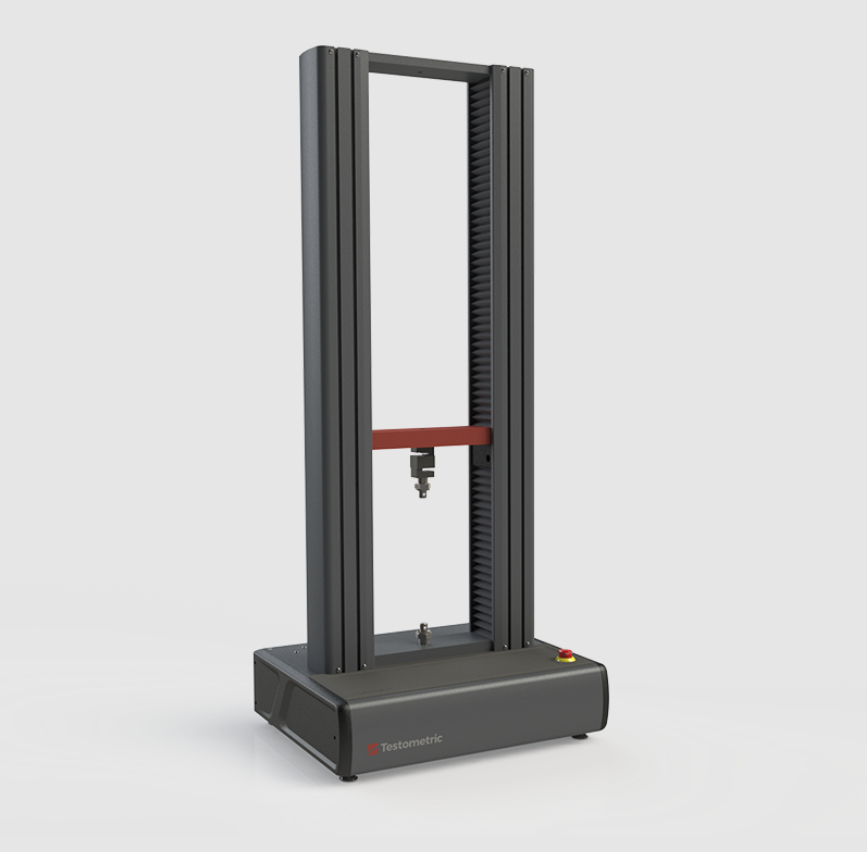
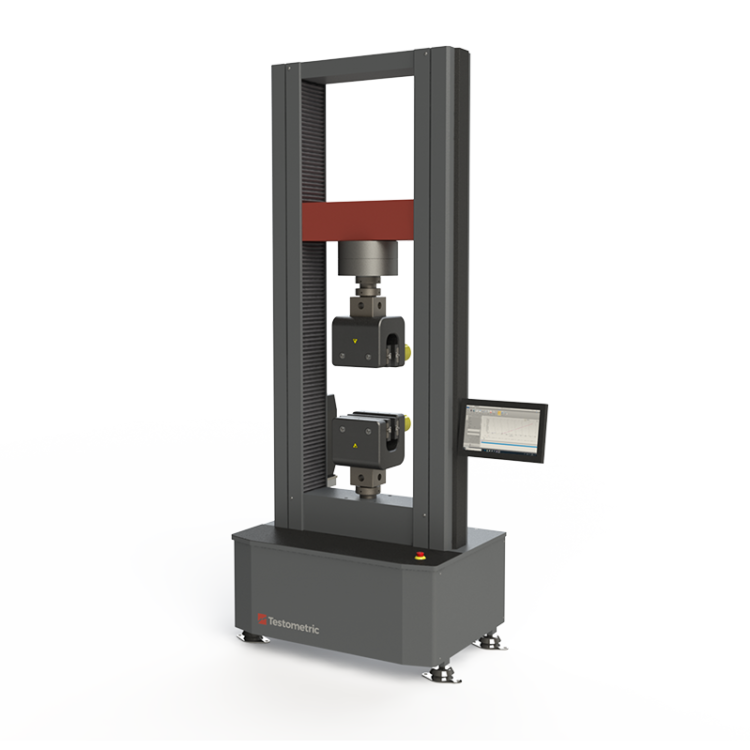
Description
Precision crosshead control via digital AC servo drive and brushless servo motor giving maintenance free operation and 23-Bit positional control.
High speed data collection systems for up to 4 synchronous channels.
6 I/O channels for additional devices such as extensometers, micrometers,
calipers, balances etc.
High stiffness loading frames with solid specialised steel crossheads and rigid extruded support columns with T-slots for accessory mounting.
Overload, overtravel and impact protection.
Telescopic covers giving additional protection for ballscrews against dust
and testing debris. Small footprint design, giving economy of bench and floor space.
Extensive range of grips and fixtures for tension, compression, flexural, shear, peel and product testing etc.
A wide range of contacting and non-contacting extensometers is available
including laser and video models.
STANDARD SPECIFICATION
| Machine Capacity | 20kN |
| Speed Range | 0.00001 to 1000mm/min |
| Crosshead Travel (excluding grips) | 1100mm |
| Distance Between Columns mm | 320 (or 420mm with wide frame option) |
BUILT FOR PRECISION
Force Measurement
Universally Calibrated, better than Grade 0.5 EN 7500-1, DIN 51221 ASTM E-4. AFNOR A03-501. Range 0.4% to 100% minimum. Automatic identification of load cell. Resolution 1 part in 500000. Electronic load cell protection.
Extension Measurement
Full frame length to a maximum resolution of 0.000001mm (selectable). Accuracy +/- 0.01mm. Absolute, relative and auxiliary modes in mm, inch and percent.
Speed Control
Class-leading low speed performance with speeds down to 0.00001mm/min. Drive system temperature and current protection.
Electronics System
Modular electronics system offers fast data transfer to the PC (up to 1000Hz) via high-speed Ethernet connection. Extensive input options allow the connection of a wide range of extensometers and accessories via simple plug-in interface modules.
OPTIONAL TOUCHSCREEN PANEL PC
When paired with the optional IPC3 industrial-grade Panel PC with touchscreen control, the machine becomes a robust standalone system without the need for an external PC or Laptop.
Using the latest Windows 10 operating system and running a full version of Testometric’s winTest software the system allows complete control of the test machine and provides storage and access to unlimited test methods and results. The included mounting arm which attaches to the machine column T-Slots is fully adjustable for height, reach and viewing angle allowing the user to find the most ergonomic working position.
SOFTWARE
Comprehensive winTest™ Analysis universal windows software covering tensile, compression, peel, shear, tear, cyclic, creep and multi stage testing. It includes a wide range of industry standard test methods and facility to create and store an unlimited number of further test methods. There is automated storage of all test data and ease of export to other software packages such as word, excel, access and SPC systems for enhanced report generation.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Force | Energy to Break | Density | Plastic Strain Ratio r |
| Average Force / Width | Energy to Yield | Chewiness | Spring Rate Between Forces |
| Bending Modulus | Initial Modulus | Fracturability | Spring Rate Between Deflections |
| Crush Force (Edge) | Force @ Peak | Hardness | Young’s Modulus |
| Deflection @ 1st Collapse | Force @ 1st Collapse | Poisson’s Ratio | Chord Modulus |
| Deflection @ Force (Stage) | Force @ Elongation | Plastic Strain Ratio r | Tangential Modulus @ Strain |
| Dynamic Co-eff of Friction | Force @ Proof | Spring Rate Between Forces | Tangential Modulus @ Stress |
| Elongation @ Break | Force after Stage | Spring Rate Between Deflections | Secant Modulus @ Strain |
| Energy to Break | Lowest Force | Young’s Modulus | Secant Modulus @ Stress |
| Energy to Yield | Seam Opening Force | Chord Modulus | Strain @ Limit of Proportionality |
| Initial Modulus | Seamed Strength | Tangential Modulus @ Strain | Force @ Rupture |
| Force @ Peak | Static Co-eff of Friction | Tangential Modulus @ Stress | Strain @ Rupture |
| Force @ 1st Collapse | Strain @ Break | Secant Modulus @ Strain | Average of 5 Highest Peaks |
| Force @ Elongation | Strain @ Force (Load Cycle) | Secant Modulus @ Stress | Bend. Strength @ Peak |
| Force @ Proof | Strain @ Force (Return Cycle) | Strain @ Limit of Proportionality | Bursting Strength |
| Force after Stage | Strain @ Force (Stage) | Force @ Rupture | Average Peaks (Selected Region) |
| Lowest Force | Stress @ Peak | Strain @ Rupture | Percentage Reduction of Area |
| Seam Opening Force | Stress @ Proof | Average of 5 Highest Peaks | Secant Stiffness |
| Seamed Strength | Stress @ Strain | Bend. Strength @ Peak | Stress @ % Height |
| Static Co-eff of Friction | Stress @ Yield | Bursting Strength | Force @ Time |
| Strain @ Break | T.E.A. | Average Peaks (Selected Region) | Deflection @ Time |
| Strain @ Force (Load Cycle) | Tenacity | Percentage Reduction of Area | Time to Peak |
| Strain @ Force (Return Cycle) | Transverse Rupture Strength | Secant Stiffness | Time to Failure |
| Strain @ Force (Stage) | Unseamed Strength | Stress @ % Height | LOP |
| Stress @ Peak | Young’s Modulus | Force @ Time | MOR |
| Stress @ Proof | Chord Modulus | Deflection @ Time | Strain to LOP |
| Stress @ Strain | Tangential Modulus @ Strain | Time to Peak | Strain to MOR |
| Stress @ Yield | Tangential Modulus @ Stress | Time to Failure | Ym |
| T.E.A. | Secant Modulus @ Strain | LOP | Average of 5 Highest Peaks |
| Tenacity | Secant Modulus @ Stress | MOR | Spring Rate Between Forces |
| Transverse Rupture Strength | Strain @ Limit of Proportionality | Strain to LOP | Density |
| Unseamed Strength | Force @ Rupture | Strain to MOR | Chewiness |
| Young’s Modulus | Strain @ Rupture | Ym | Hardness |
| Chord Modulus | Average Peaks (Selected Region) | Average of 5 Highest Peaks | Poisson’s Ratio |
| Tangential Modulus @ Strain | Percentage Reduction of Area | Spring Rate Between Deflections | Plastic Strain Ratio r |
| Tangential Modulus @ Stress | Spring Rate Between Forces | Density | Spring Rate Between Deflections |
| Secant Modulus @ Strain | Spring Rate Between Deflections | Chewiness | Young’s Modulus |
| Secant Modulus @ Stress | Chewiness | Hardness | Chord Modulus |
| Strain @ Limit of Proportionality | Fracturability | Poisson’s Ratio | Tangential Modulus @ Strain |
| Force @ Rupture | Hardness | Plastic Strain Ratio r | Tangential Modulus @ Stress |
| Strain @ Rupture | Plastic Strain Ratio r | Spring Rate Between Forces | Secant Modulus @ Strain |
| Average of 5 Highest Peaks | Spring Rate Between Deflections | Density | Secant Modulus @ Stress |
| Bend. Strength @ Peak | Young’s Modulus | Chewiness | Strain @ Limit of Proportionality |
| Bursting Strength | Average Peaks (Selected Region) | Hardness | Force @ Rupture |
| Percentage Reduction of Area | Poisson’s Ratio | Strain @ Rupture |
| Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Adhesives | Packaging |
| Automotive | Food | Cord and Rope |
| Cable and Wire | Pipe | Elastic |
| Clothing | Adhesive tape | Geotextiles |
| Containers | Credit Cards | Medical |
| Military | Constructions | Rubber |
| Bedding | Cargo Restraints | GRC |
| Toys | Concrete | Rope & Nets |
| Fibre | Metals | Insulation |
| Foam | Furniture | Footwear |
| Timber | Springs | Plastic film and sheet |
| Wood based Panel | Yarn & Cord | Corrugated board & Boxes |